
| Genre: | Compilation Of Arcade Games |
| Publisher: | Acornsoft |
| Contents: | |
| Cover Art Language: | English |
| Machine Compatibility: | Acorn Electron |
| Release: | Professionally released on Cassette |
| Compatible Emulators: | Elkulator 1.0 (PC (Windows)) |
| Original Release Date: | 1st September 1983 |
| Original Release Price: | £9.20 |
| Market Valuation: | £0.76 (How Is This Calculated?) |
| Item Weight: | 106g |
| Box Type: | Cardboard Box (Decorative) |
| Author(s): | A. J. Reeve |
Variant Items
There are 0 other items featuring this same game (that we know about!). Click any of them for their details.
Active Auctions
Closed Auctions
Buy It
Unfortunately no-one is currently selling this item.
However, this item has previously been sold on everygamegoing.com, so there is a good chance it will be offered again. Add it to your Wanted Items to be notified immediately anyone offers it for sale.
Auction Price Watch
Worried you're being ripped off? Closing prices on eBay can help you decide what a reasonable price is for a particular item.
Full Instructions
Introduction
Business Games contains two educational games. Although intended for use in business and economic studies, teaching the games are entertaining and thought-provoking in their own right.
This guide describes the two programs that make up Business Games.
STOKMARK, which simulates the conditions of the stock market, with realistic behaviour of share prices based on an analysis of real companies.
In TELEMARK, four teams or players each control the finances of a firm that makes and sells televisions.
In both these games each player in turn will be prompted either to select an option (for example, Yes or No) or to enter numbers or letters: the RETURN key should be pressed after each selection or input.
STOKMARK
This is a game for between one and eight players, each of whom tries to make as large a profit as possible by buying and selling shares on the stock exchange.
How To Play
- Once the program has been loaded step through the introductory screens by pressing SPACE as prompted. You will then be prompted to type in the number of players (1-8) and their names. (Remember to press RETURN after entering each name.) The order in which the names are entered will be the order of play throughout the game.
The DELETE key can be used to correct typing mistakes while entering data, but after you have pressed RETURN mistakes cannot be rectified.
-
Each player starts with £1200 which can be used to buy in stock initially. The computer asks each player in turn how they will trade. In response to the question "Which shares will you trade?", reply by selecting one of C, D, E or F, and then type in the number of shares you want to buy.
For example, to buy shares in Electrix enter E, followed by the number of shares you wish to buy as prompted by the computer.
- In subsequent rounds the computer asks whether you want to buy or sell according to whether you possess shares or not. After specifying the kind of shares (C, D, E or F) and typing B or S to buy or sell, type in the number of shares you want to trade.
- After the third round a valuation is given, showing who is 'worth' the most in terms of capital and shares owned; this person is in the lead. (Rounds are numbered in the top right-hand corner of the screen.) Dividends are paid after every fourth round, and displayed as shown below:
DIVIDENDS PAID C) Colemine pays 10 per cent D) Derfoods pays 11 per cent E) Electrix pays 15 per cent F) Fintrust pays 12 per cent DIVIDENDS RECEIVED (C) (D) (E) (F) Total Jonathan 15 29 21 42 108 Sarah 8 19 0 12 39 Dave 27 14 18 42 102 Pippa 12 13 0 36 61 Press SPACE BAR to continue - News of current events and company news affecting share prices is displayed at intervals during the game.
- If a player does not want to trade when their turn comes round they can type M to miss a turn.
- The first player or team to reach a valuation of £5000 is the winner.
Explanation Of Terms
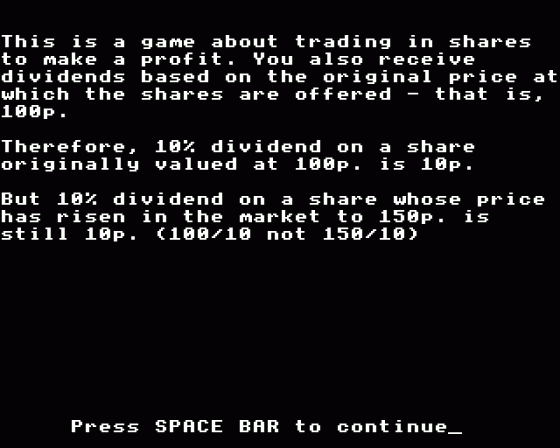
Dividend = If a person invests their money in a company by buying shares, they can expect a return on their investment in the form of a share of the profits. This share of the profit is referred to as a 'dividend'.
In this game, all the companies declare half their profits as dividends, and calculate their value as a percentage of the original share price (i.e. 100p since all shares are 100p to start with). Dividends are paid after every fourth round.
Price = The current market price of the shares.
Price to Earnings ratio = The P/E is the ratio of the market price of the share to its earnings in terms of profit. In other words P/E = Price per share DIV Profit per share. A low P/E is a sign of high profits in relation to price.
Punter = A small gambler on the Stock Exchange.
Yield = When trying to assess the performance of shares the yield is an important indicator of their worth. You will see that initially the yield of all shares is the same (10), but the yield of the shares will fluctuate during the game. The yield is calculated as: Yield = (Nominal value x dividend) DIV Market price.
As the game progresses you will see the yield fluctuate according to how the current market price changes in relation to the original 'nominal' value of 100p. Notice that a high market price does not in itself give an increased yield, but high dividends will always work in favour of the yield.
Some General Advice
When buying shares, use the Price to Earnings ratio and the Yield to assess their performance.
As a general rule, the price of shares will increase when they are bought, and will decrease when they are sold; such is the law of supply and demand, where something which is sought after becomes less available and more expensive, and something which is not in demand becomes more readily available and cheaper in price.
TELEMARK
The object of this game is for each of four players or teams to try to make the largest total profits, or to win more than half the market share of televisions.
How To Play
-
Once the game has been loaded step through the introductory screens by pressing SPACE as prompted. Then name the players as prompted by the computer. (Remember to press RETURN after entering each name.) The order in which names are entered will be the order of play throughout the game.
The DELETE key can be used to correct typing mistakes while entering data, but once RETURN has been pressed, mistakes cannot be rectified.
- Every player starts off with 2165k (the letter 'k' means £1000). All numbers are rounded down to whole thousands on the screen to keep it simple, but are stored in the computer as pounds.
- The computer will keep accounts for each players, but you may find it helpful to work out a break-even chart on paper along the lines of the sample break-even analysis detailed shortly. Some blank charts (including charts for a break-down of cash flow) are stapled into this booklet for your use.
- The computer asks each player to make various decisions, the first few of which require Yes/No answers. Select Y or N, or alternatively, type Q (Query) for information.
Allocating Funds
-
The first decision to be made is whether to build a factory for 1000k and then whether to build an extension.
When you buy a factory or an extension half the money is spent on buildings, and half on plant or machinery. Buildings retain their value in full, but there is 10% depreciation on machinery, and this is taken into account when calculating profit at the end of each round.
-
There is space in the factory to build or store 12 batches of televisions, and an extension provides sufficient space for four more batches.
Every player starts off with twelve market shares, which correspond to the maximum capacity of the factory to begin with - i.e. to produce and store twelve batches of televisions.
To expand, you need an extension, which will provide room for four further batches, and you need to bid for a larger market share by spending 25k on extra marketing. Thus if a player decides to produce a larger number of TVs than their current market share, they are asked whether to not they would like to bid for more market shares.
- As in real life, there is an element of chance in the game. A decision to spend on better management could result in improvements to the firm's performance, but equally, could gain nothing, or even result in the threat of a strike for which the player is penalised. The chances of suffering a penalty in the first two rounds is nil, but chances increase in later rounds.
- In each round the computer detects a sum for overheads. These consist of bills for the rates, electricity, transport and so on, and the amount varies according to the size of the firm.
Working Out A Selling Price
You can charge anything between 1 and 50 for your televisions. Avoid letting the other players see the price you type in (the number itself will not be displayed on the screen).
If you are somebody who does not like to leave these things to chance, then it is worth working out a break-even price for your TVs as shown in this example:
Break-Even Analysis
1) Work out depreciation and plant value e.g.
New factory 1000
Extension 400
----
CAPITAL SPEND (subtotal) 1400
Capital Spend DIV 2 (for plant) 700
Add the old plant value 0
Plant value DIV 10 (for DEPRECIATION) 70
----
NEW PLANT VALUE 630
----
2) Add up your planned current spend
Opening stock value 0
Management 25
Risks 0
Overhead
factories @ 120k each 120
extensions @ 10k each 10
16 batches of TVs @ 20k each 320
Market bids @ 25k each 25
----
CURRENT SPEND (total) 500
----
3) Add depreciation
Depreciation 70
----
TOTAL COSTS 570
----
4) Divide by how many you might sell
Total costs/market share (e.g. 12) 47
Total costs/market share +4 36
Total costs/market share -4 71
5) Decide how many you will sell
6) Less innovations @ 2k each 0
----
7) = BREAK-EVEN COST (e.g. for 16) 36
----
8) Add PROFIT (say 4) 4
----
9) = SELLING PRICE 40
The break-even price, as its name implies, is the lowest price you can charge and still cover your costs. Once you know what the break-even price is, you can decide on a price that you think the market can bear, and which allows you some profit. Bear in mind, however, that the higher the price the more risk there is of losing market shares.
If you charge less than 1 the computer sets up a black market to raise your price to 50. If you charge more than 50 then an importer takes all your market shares with a price of 51.
If you have won any innovations they are worth 2k for every batch you sell and the computer takes this into account when calculating your profit.
When you have input prices, the computer compares them and decides how many you actually sell.
If you have bid for extra market shares and your prices is lowest you might gain four more market shares, in order words sell 16 TVs instead of 12. But if your prices is highest you might lose 4 market shares. It is possible to lose more than 4 under certain circumstances.
The computer finally displays a series of four information sheets which compares the performance of all four players; notes on these are given below.
When each player or team has examined their finances, and decided on a strategy for the next round, the game continues.
Market Shares Report
This shows the proportion of the market currently held by each player, and is based on the number of TVs they have sold. The number of TVs sold by a player is calculated by the computer on the basis of how their selling price compares with the prices set elsewhere in the market.
The winner of the game is the player or team who succeeds in winning over 24 market shares.
MARKET SHARES REPORT
4 8 12 16 20 28 32
___*___*___*___*___*___*___*___*
Simon 12 XXXXXXXXXXXX
Neil 8 XXXXXXXX
Cathy 10 XXXXXXXXXX
Tim 16 XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Profit And Loss Account
This gives each player's profit or loss figure for the round, which can be calculated as follows:
- Deduct production expenses from the revenue (money obtained from the sale of televisions) to discover the profit before depreciation.
- From this figure deduct 10% depreciation, to obtain the profit or loss figure.
Total Profit
This gives an overall view of the amount of cash each player has (with loans subtracted) and the total profit during the course of the game.
Balance Sheet
A company's balance sheet summarises its financial position by showing all that it owes, including what it owes to its shareholders (or liabilities) in one column and all that it possesses (or assets) in another column. The two columns must add up to the same amount, being balanced by total profit or loss. Here the balance sheet is abbreviated to show the major items as they appear in the game.
As a training exercise you might like to work out your own profit and balance sheet, and check it against the computer's.
Screen Designers
The following utilities are also available to allow you to edit the supplied screens of this game:
Cheats
Download
A digital version of this item can be downloaded right here at Everygamegoing (All our downloads are in .zip format).
| Download | What It Contains |
|---|---|
| A digital version of Business Games suitable for Elkulator 1.0 (PC (Windows)) | |
| A digital version of Business Games suitable for Elkulator 1.0 (PC (Windows)) | |
| A digital version of Business Games suitable for Elkulator 1.0 (PC (Windows)) |
Report A Problem
We thank you from the bottom of our hearts if you report something wrong on our site. It's the only way we can fix any problems!
You are not currently logged in so your report will be anonymous.
The 1 most recent sales for this item are as follows:
| Date Sold | Price Sold For | As Part Of Bundle | By User |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31st March 2024 | £1.49 | No | dave_e |
Add Note
Release Country
Change the country to update it. Click outside of this pop-up to cancel.
Scan Of Selected Article
If you auction an item, it will no longer show in the regular shop section of the site.






















